About the Project
Hong Kong Mosquito Issues
WHAT PROBLEM ARE WE TRYING TO SOLVE?
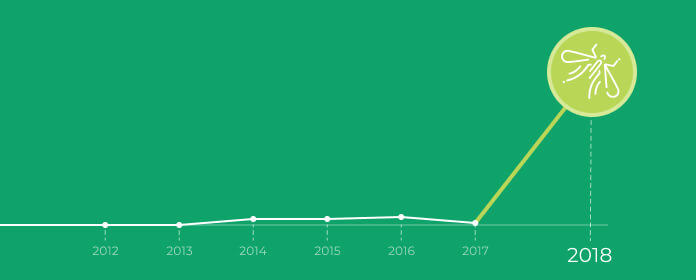
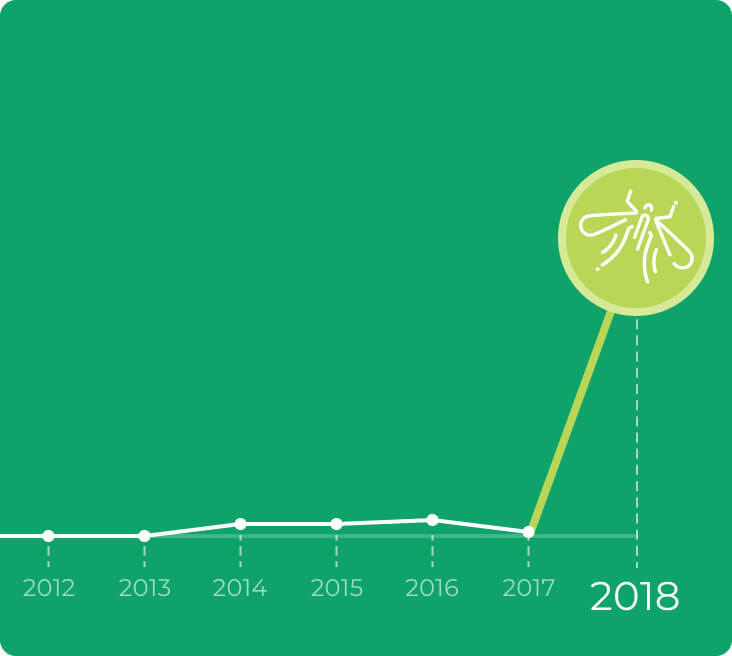
Before, most mosquito-borne illnesses in Hong Kong were imported cases. Climate change has increased global temperature, increasing the risk of dengue fever, malaria, and Japanese encephalitis in Hong Kong. Mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue fever ("dengue"), Zika virus and malaria may pose public health threats, even in developed places.
Higher temperatures encourage disease-carrying Aedes mosquitoes to breed, leading to faster growth and longer survival periods. Warmer temperatures also shorten dengue fever's incubation period.
More record-breaking hot years in Hong Kong and an increase in imported and local dengue cases are expected to strain local healthcare systems.

WHAT TO DO?
Mosquito prevention and control efforts involve deploying traps to sample the mosquito population to enhance surveillance and controlling mosquitoes by chemical means or source reduction of potential habitats. (Passive and Slow)
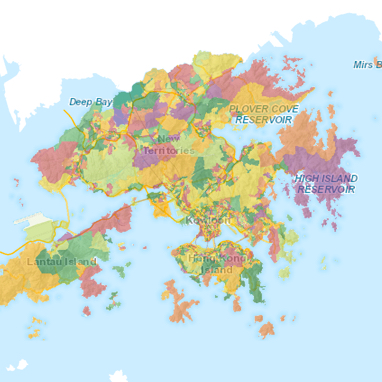
In Hong Kong, HKSAR Food and Environmental Hygiene Department (FEHD) will only monitor the dengue vector Aedine mosquitoes and report the Gravidtrap index in selected areas of Hong Kong every 2 to 4 weeks. A real-time monitoring system with faster dengue data announcements throughout Hong Kong is vital. It gives the public up-to-date information on high-risk areas and improves FEHD's and other government departments' location-based decision-making and planning.
Program’s Background
A Smart Intelligent GeoAI Solution to Predict & Tackle Mosquito-borne Diseases in Hong Kong

The project is supported by the HKSAR Food and Environmental Hygiene Department and funded through the Partnership Research Programme of the HKSAR Government's Innovation and Technology Fund (ITF).
Its goal is to create a real-time smart and predictive mosquito monitoring solution in Hong Kong, to enhance mosquito surveillance and provide more user-friendly information through a timely interactive maps to highlight more severe mosquito hotspots.
The system will use cutting-edge smart technologies such as IoTs, GIS, GeoAI, and Deep Learning algorithms to monitor, address, and anticipate the occurrence of mosquito-borne diseases in Hong Kong based on geographical location.
The ultimate goal is to improve the effectiveness of mosquito-borne disease monitoring, thereby contributing to better disease management through community engagement.
Find out moreOur Objectives

01
Real-time
Develop a sophisticated, real-time system for Hong Kong mosquito monitoring
02
AIoT
Adopt IoTs, GIS, GeoAI, and Deep Learning methods to monitor, address, and anticipate mosquito-borne diseases by location in Hong Kong

03
Big Data
Intend to shorten FEHD’s mosquito reporting time, enhance the efficacy of big data collection and transform the legacy of mosquito monitoring to better estimate disease endemic zones

04
Community-based
Improve mosquito-borne disease monitoring efficiency for better community-based disease management
Real-time
Develop a sophisticated, real-time system for Hong Kong mosquito monitoring
Project Team Members
Prof. Paulina Pui-Yun Wong
Lingnan University
Prof. Man-Leung Wong
Lingnan University
Dr. Kester Kwan Yeung Li
Lingnan University
Dr. Rosiah Ho
Lingnan University
Mr. Pui Keung Cheung
Lo's Enviro-Pro Holdings Limited
Mr. Andrew Tsang
Triple Faith Engineering
Mr. Vincent Chow
Triple Faith Engineering
Mr. Pak Ming Leung
Project Manager (Hardware)
Mr. Boris Wong Ka Chun
Project Manager (Software)
Ms. Wenhui Cai
Research Officer
Mr. Paxton Leung
Research Officer
Mr. Minhao Li
Research Officer
Mr. Issac Ng
Research Officer
Ms. Linfei Zhang
Research Officer